THE YELLOW FEVER VACCINE
WHAT IS YELLOW FEVER ?
Yellow fever is an acute viral hemorrhagic disease, which is transmitted through the bite of a contaminated mosquito. The disease has an incubation period of 3 to 6 days.
The symptoms of yellow fever include a fever, chills, headaches, back ache, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and muscular pain. Most of the persons infected with yellow fever recover after 3 to 4 days. But 15% of the affected people experience a second phase of the disease, more toxic, in the 24 hours following the initial recovery. Fever returns and severe symptoms appear, such as bleeding from the mouth, the nose, the eyes and the stomach, a jaundice, abdominal pain, vomiting and renal failure. At this stage, blood is usually observed in the vomit and in the feces of the victim. Half of the persons experiencing this toxic phase die within 10 to 14 days. The rest of the people recover with no severe organ damages.
WHAT IS THE RISK FOR TRAVELERS ?
Every year, 200 000 cases of yellow fever are reported in the world, including 30 000 deaths, most of them occurring in Africa. Yellow fever is endemic in 31 countries in Africa and in 13 countries in Latin America (in Bolivia, in Brazil, in Colombia, in Ecuador and in Peru notably). In Asia, no cases of yellow fever have been reported. In North America and in Europe, outbreaks have occurred in the past centuries, but these areas are free of yellow fever nowadays. All the travelers going to a country at risk may be infected by the disease.
HOW TO PREVENT YELLOW FEVER ?
There is a vaccine for yellow fever. If you are traveling to a country where the disease is endemic, you must consider it. See a doctor prior to your departure, he/she will help you to know if you need the vaccine. Note that some countries (even if they are not affected by the disease) require a proof of vaccination against yellow fever before they grant travelers an entry visa, to prevent the importation of the yellow fever virus on their territory.
- In addition to the vaccine, you must protect yourself efficiently against mosquito bites while traveling.
- Wear protective clothes, such as long pants, long-sleeved shirts and hats.
- Apply mosquito repellent on exposed skin. You should preferably use a repellent offering long lasting protection and containing a high percentage of active ingredients, such as DEET, Picaridin or IR3535. Use repellents carefully and always follow product instructions. In particular, avoid applying repellent in your eyes, in your mouth and on your hands. You can combine sunscreen and insect repellent, just apply the sunscreen first.
- For optimal protection, use Permethrin-treated clothing and gear. You can purchase pre-treated items in specialized shops, but you can also treat your own clothes and equipment, such as pants, socks, boots and tents. Handle Permethrin with caution and avoid any direct contact with your skin. Permethrin remains effective, even after several washes.
- Stay in air-conditioned environments whenever possible.
- Always sleep under a mosquito net, especially if your room is exposed outdoors or if you sleep outside.
What Are The Symptoms Of Yellow Fever?
Most people will start to experience symptoms of yellow fever within the first three to six days following their infection. The majority of individuals will only experience the initial series of symptoms that have been associated with yellow fever. A small portion of infected may experience more severe symptoms – approximately 15% of all infected individuals develop serious complications and dies within the first two weeks following the infection.
The initial symptoms associated with the yellow fever infection may include:
- Fever and chills
- Headaches
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- A loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea, often accompanied by vomiting
- Back pain
- Weakness and fatigue
- Dehydration
When a patient does not recover during the initial phase of yellow fever, then they may develop the following potentially life-threatening complications:
- Internal bleeding
- Jaundice
- Shock
- Organ failure
What Are The Treatment Protocols For Yellow Fever?
The healthcare system has not yet developed a specific type of medication that can treat the virus that causes yellow fever. This, however, does not mean no treatment protocols can be initiated when an individual is infected. Prompt medical care can provide the affected individual with supportive care to assist with alleviating the symptoms caused by the infections. It is also vital for the infected to be treated with appropriate techniques to help restore optimal hydration levels in their body, as the dehydration caused by yellow fever can lead to unpleasant complications. Supportive care can also look for organ failures, such as kidney or liver-related issues, and provide prompt treatment to assist in such conditions.
How To Prevent Yellow Fever?
Several informational sites and campaigns have been launched to make the public aware of the fact that prevention is critical when travelling to a yellow fever risk site. Several techniques can be used to prevent being infected by this mosquito-borne virus effectively. Implementing a combination of these techniques will provide a person with better results and a higher level of protection against the infection.
The Yellow Fever Vaccine
The first and most effective preventative approach to yellow fever is the official vaccine that has been approved for reducing the risk of being infected when travelling to a high-risk location. This vaccine needs to be administered to a person before they visit their travel destination. The yellow fever vaccine has been proven effective to prevent a person from being infected with this virus, which provides a much more efficient approach as compared to being infected and initiating appropriate therapies.
Who should get the yellow fever vaccine?
The yellow fever vaccine is highly recommended for any person who will be travelling to a destination that is listed as a high-risk area for the yellow fever virus. Individuals who are planning to travel should ensure they do some research before their travelling to find out whether their destination is considered a high-risk region.
Who should not get the yellow fever vaccine?
This vaccine is not appropriate for everyone. Individuals who are planning a trip need to consult with a facility close to them to find out if a yellow fever vaccine will be safe and effective for them. In particular, every individual need to be tested for allergy first as an allergic reaction to the yellow fever vaccine can be harmful.
- Other indications for individuals that will usually not qualify for a yellow virus vaccine include:
- Babies who have not yet reached the age of six months.
- Patients who have undergone organ transplantation.
- Patients diagnosed with primary immunodeficiency, malignant tumor, and thymus disorder.
- Patients who are undergoing immunomodulatory therapy or taking immunosuppressive agents.
- Patients with HIV.
What is the minimum age requirement for yellow fever vaccine?
Individuals should note that babies and children are able to obtain the yellow fever vaccine, but not if they are younger than six months. Additionally, when a baby is between the age of six to eight months, the use of a yellow fever vaccine should first be discussed with a healthcare provider. This shot is generally considered safe for babies over the age of eight months.
How long before travelling do you have to get yellow fever vaccine?
The yellow fever vaccine takes approximately ten days to become effective and help the patient’s immune system build up an immunity against the virus that causes this infection. Thus, when planning a trip, a person should get this vaccine at least ten days in advance before they go on the trip.
How long does yellow fever vaccine last for?
A single shot of the yellow fever vaccine is enough to provide adequate protection for a person who will be travelling to a destination that will place them at risk of this infection.
For many individuals, a single shot may provide them lifelong prevention of the yellow fever virus. It is, however, often advised that a person obtains a booster shot every decade to ensure effective immunity against the virus.
What are the side-effects of the yellow fever vaccine?
Individuals obtaining the yellow fever vaccine should be aware of certain side-effects that may develop after they have obtained the vaccine. These side-effects may last for up to 10 days after a person has been vaccinated.
Some of the most common side-effects that are considered normal and not serious include:
- Mild headaches
- A low fever
- Muscle and joint pain
- Body aches
- A lump at the vaccination site
- Pain and tenderness in the vaccination site
- A general feeling of being ill
There are more serious adverse reactions that may also develop. In such a case, the patient is advised to contact their doctor. These side-effects may include:
- Flu-like symptoms, including vomiting, a loss of balance, irritability, confusion, a stiff neck and a stiff back.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Severe pain in the lower back.
- Problems with bowel or bladder control.
- Severe muscle weakness.
- Seizures.
- Behavioral changes.
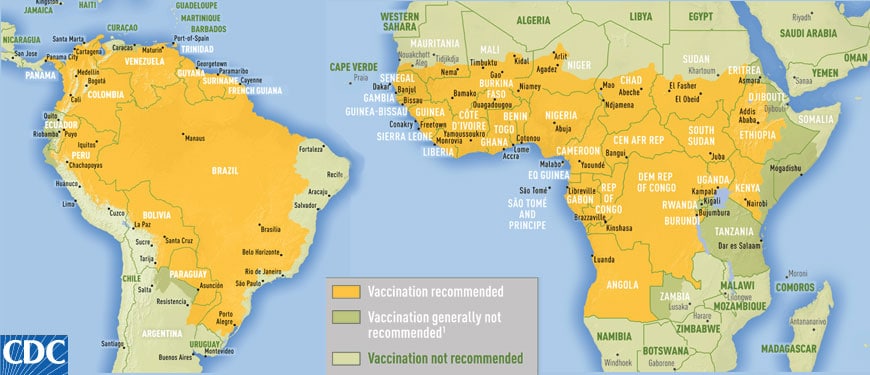
What Areas Are At High Risk for Infection?
Yellow fever is not common in all areas of the world and is more restricted to specific regions as compared to some other mosquito-borne diseases, such as malaria. Yellow fever is most commonly found in certain locations within Africa and South America.
In South America, the following locations are considered to be at a high-risk for yellow fever infections:
- Argentina
- Bolivia
- Brazil
- Colombia
- Ecuador
- French Guiana
- Guyana
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Suriname
- Trinidad
- Venezuela
A much larger region of the African continent is considered to be areas that put a person at a risk of being infected with this virus during their travels. Locations in Africa with the highest risks associated with them include:
- Angola
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Central African Republic
- Republic of the Congo
- Equatorial Guinea
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea / Guinea-Bissau
- Liberia
- Nigeria
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- South Sudan
- Togo
- Uganda
How To Obtain A Yellow Fever Vaccine?
Individuals who are planning to travel to an area that is known to be at risk for yellow fever need to ensure they obtain a yellow fever vaccine before their travels. The Public Health Agency of Canada provides a list of approved health care centers where vaccines can be obtained. It is essential to contact only authorized health care centers in advance to ensure a vaccine can be available for an individual who is planning to travel to affected sites.
Yellow Fever Vaccinations With Summit Health
The yellow fever infection can cause life-threatening symptoms to develop, making the prevention of the infections the most appropriate approach to treatment.
Preventing yellow fever can be done effectively through a number of different options, with the yellow fever vaccine being the most preferred preventative technique.
Initial research before travelling can help individuals identify the risk of yellow fever and ensure they take appropriate precautionary measures to prevent them from becoming infected.
Our travel health clinics are designated Yellow fever centres
We make every effort to ensure that the information posted on our website is up to date and accurate according to the latest public health recommendations; however, it is impossible for us to make changes on a daily basis.
For the most current travel health recommendations, please call our clinic as make an appointment with one of our travel health professionals.

